By Udhaya Shankar
Native vegetation includes those species of plants which occur naturally in a habitat and provide home to insects and animals of that region.
India is home to several types of vegetation ranging from Deciduous Forests, Tropical Evergreen Rain Forests, Dry Deciduous Forests, Mangrove Forests and Semi Desert and Desert Vegetation (Fig. 1).These species of flora have evolved over time and form a community of their own.
Native vegetation is not only help to retain local ecosystem but also increase biodiversity and habitat for other creatures of the systems. With development it is also important to maintain the system balance.
For eg: The honey bee are habitat at tropical climates and heavily forested area. They adapt to any atmosphere, but they prefer to build at garden or greener environment. But what is the relevance of these, it is because of the habitat grow at their natural state which is vanishing. But it is possible to brought back by adapting the natural vegetation same in aesthically and functionally too.
In recent times, labour intensive turf grass have taken over and is an aesthetic element of current corporate world. These days we can see turf at every corporate office landscape.
Note that the turf consumes more amount of water than the natural flora. Even the rating systems suggest having a maximum of 10% of turf in a given area.
Why should we consider native vegetation while landscaping?
- Native vegetation is well suited for the soil, temperature and rainfall of that region.
- It gradually helps restore soil quality and reduces water run off from urban areas.
- It is said to consume less water than other species.
- It can be planted at a reduced cost and requires less maintenance.
- Native plants are aesthetically pleasing.
- They provide home to the wildlife fauna of that region.
- They can be used in any garden or be a part of any landscape.
The effort of choosing the right species for landscaping will contribute in making a sustainable environment.
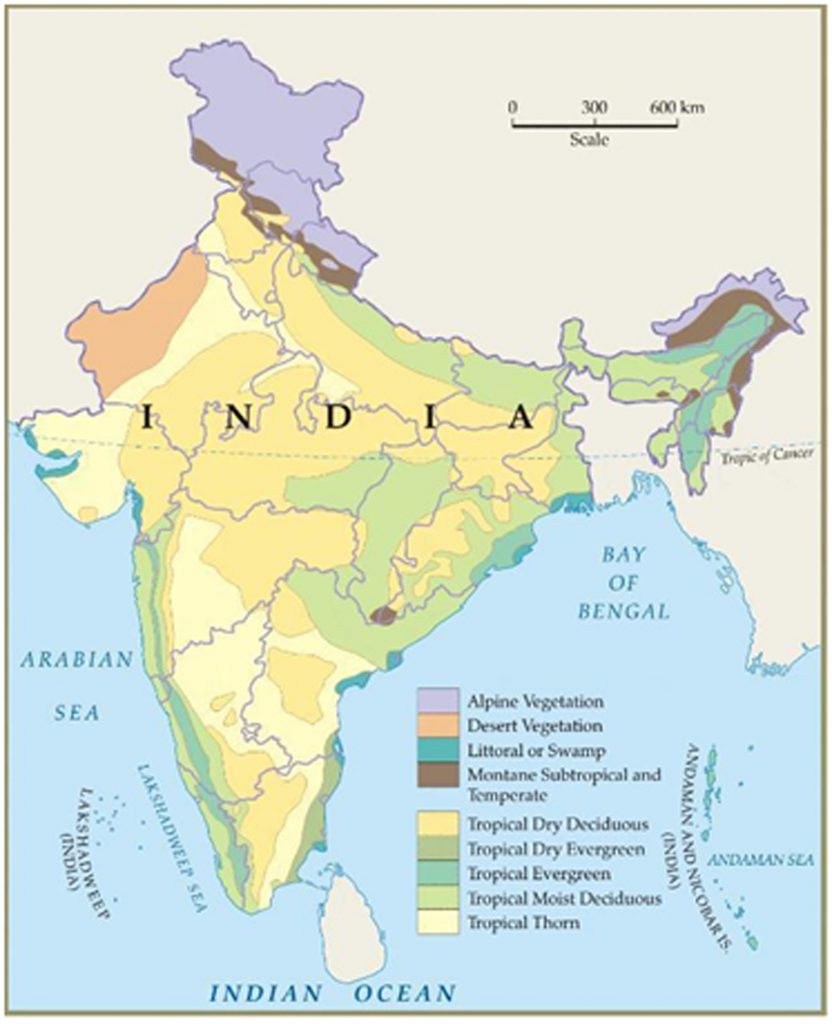
Source: http://agritech.tnau.ac.in/forestry/forest_india_types.html

Source: https://www.asla.org/nativeplants.aspx
